Diabetes occurs when the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood becomes higher than normal.
This usually happens for one of two reasons:
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that helps glucose move from the bloodstream into the body’s cells, where it is used for energy. When insulin is missing or not working effectively, glucose cannot enter the cells and instead builds up in the blood, leading to Diabetes.
In a healthy individual:
In Diabetes, blood sugar levels remain elevated and may rise dangerously high if not managed properly.
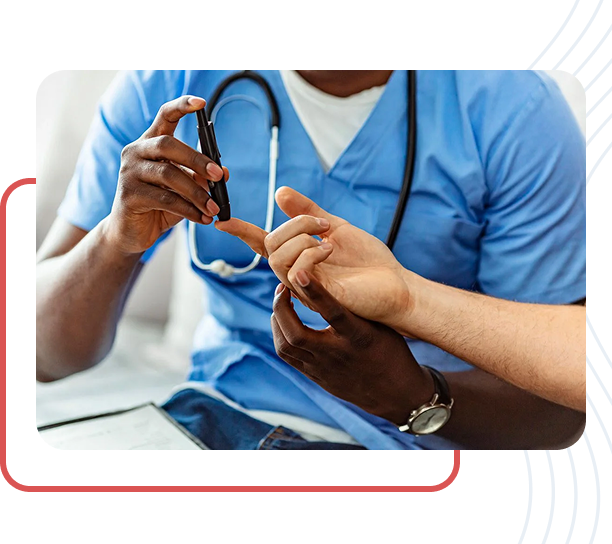

Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the body stops producing insulin. This occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Without insulin, the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Type 1 Diabetes is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, though it can develop at any age. Early diagnosis and consistent insulin therapy are essential for maintaining blood sugar control and preventing serious long-term complications.
The symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes often appear suddenly and may worsen quickly if left untreated. Common symptoms include:
Early diagnosis and regular insulin care help people manage Type 1 Diabetes safely and avoid serious health issues over time.
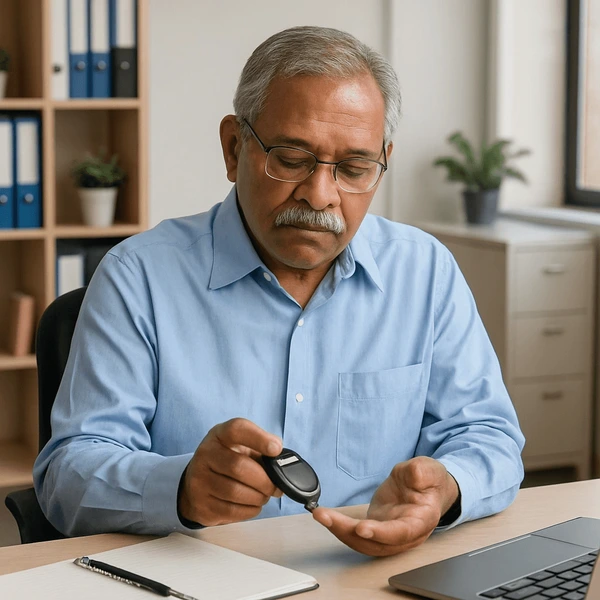


Type 2 Diabetes is a long-term condition in which the body does not use insulin effectively, a problem known as insulin resistance. Over time, the pancreas may also stop producing enough insulin, causing blood sugar levels to remain high.
It most commonly develops in adults over the age of 40, but is increasingly seen in younger people due to poor diet, lack of physical activity, excess weight, and lifestyle-related factors.
With the right combination of nutrition, physical activity, and medical care, Type 2 Diabetes can be well managed and in many cases it can be improved a lot.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes often develop gradually and may go unnoticed in the early stages. Common symptoms include:
Early awareness and everyday lifestyle changes can help keep blood sugar steady and reduce future health risks.
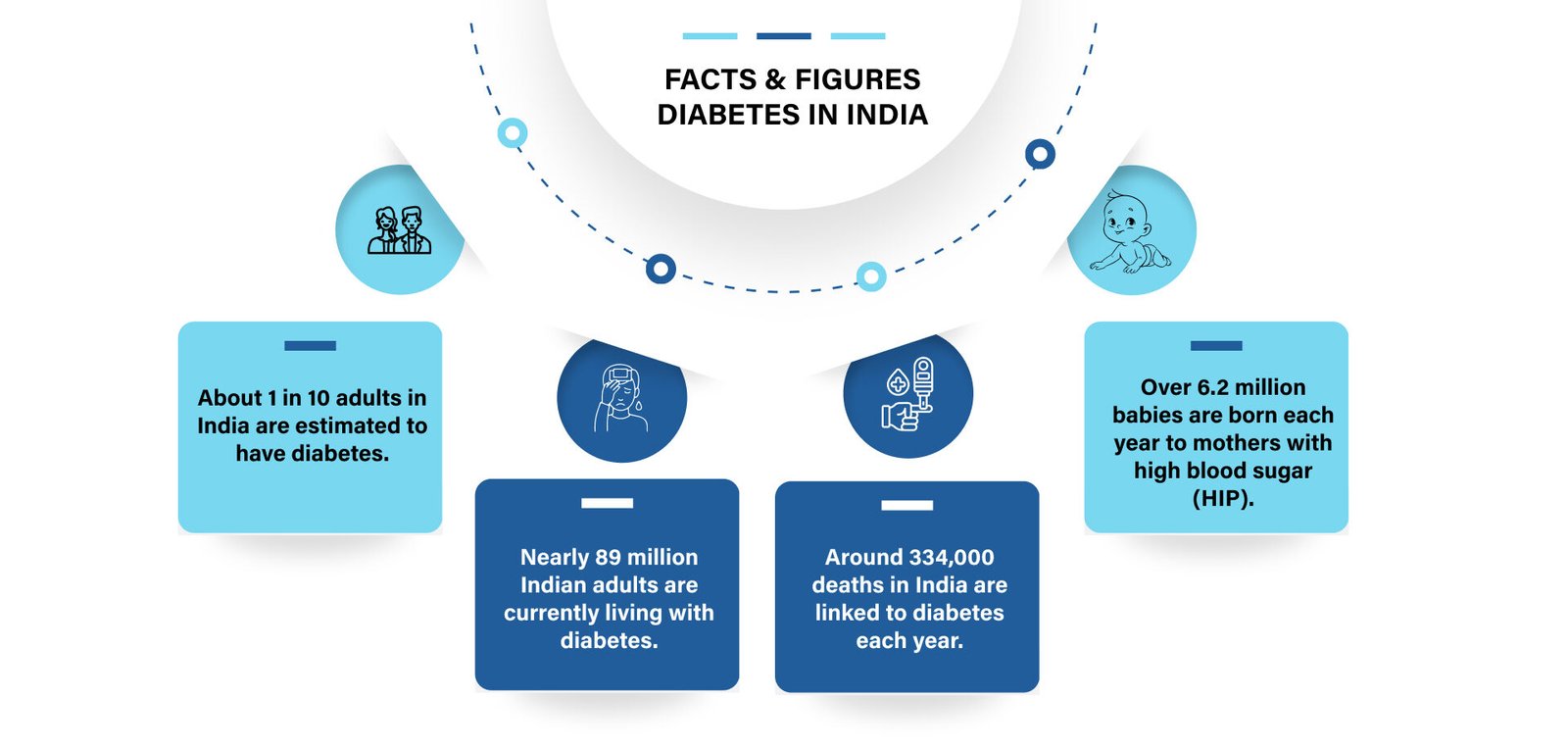
Diabetes isn’t just about numbers, it affects emotions, social life and daily choices. With the right guidance, it can be managed, prevented and sometimes even reversed.

Regular check-ups and following your doctor’s advice on medicines, insulin, and tests help keep your Diabetes on track.

The food you eat matters. You don’t need extreme diets, just simple and balanced choices, if made consistently, can support better blood sugar control.

Gentle activities like walking, yoga, or light exercise help manage blood sugar, maintain a healthy weight, and boost overall well-being.

Small, sustainable routines around food, movement, and self-care make Diabetes easier to manage and help reduce long-term complications.

Regular check-ups and following your doctor’s advice on medicines, insulin, and tests help keep your Diabetes on track.

The food you eat matters. You don’t need extreme diets, just simple and balanced choices, if made consistently, can support better blood sugar control.

Gentle activities like walking, yoga, or light exercise help manage blood sugar, maintain a healthy weight, and boost overall well-being.

Small, sustainable routines around food, movement, and self-care make Diabetes easier to manage and help reduce long-term complications.

Living well with Diabetes is about creating steady, healthy routines that support your body every day. You don’t need drastic changes, just small, consistent actions can help keep blood sugar levels balanced and improve overall health.
Join Diabetes Free Nation and receive easy-to-follow tips, nutrition advice, and daily lifestyle guidance to manage Diabetes with confidence.